Spatial computing blends digital objects with the physical world using sensors and digital maps, letting you interact naturally with virtual elements in everyday environments. It involves devices like smartphones or smart glasses that detect your position and how you move, so digital content stays aligned and responsive. This technology creates immersive, seamless experiences, making digital interactions more intuitive. Keep exploring, and you’ll discover how these innovations are transforming your daily life in surprising ways.
Key Takeaways
- Spatial computing blends digital content with the physical world for immersive, real-time experiences using sensors and mapping technology.
- Augmented reality (AR) superimposes digital images or info onto real environments, enhancing interaction and understanding.
- Sensors detect user movement and surroundings to accurately position and adjust digital objects in physical space.
- Spatial orientation helps digital content stay anchored and aligned as users move within their environment.
- Advances in sensor tech and mapping make AR more realistic, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated into daily life.
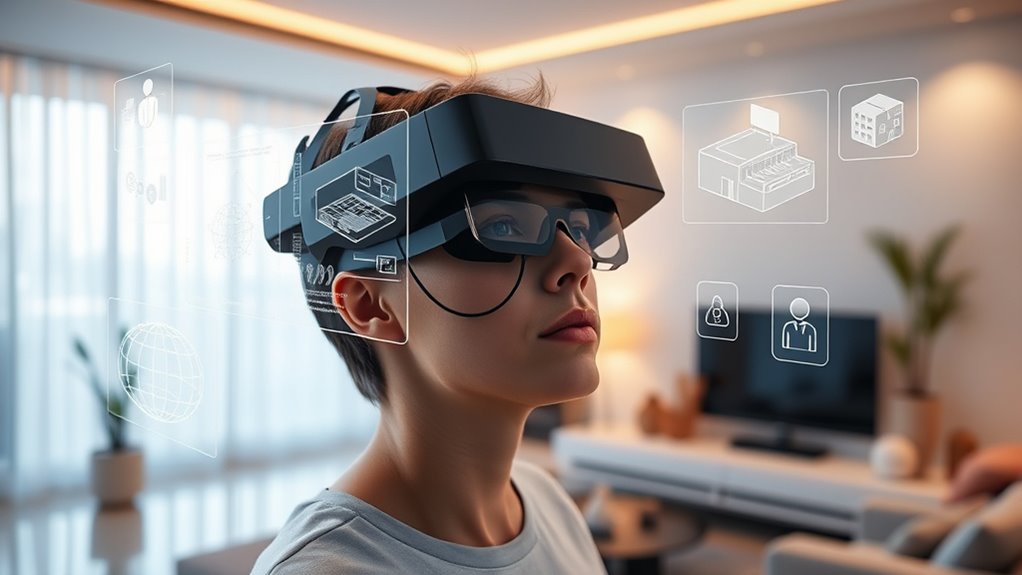

Have you ever wondered how digital objects can seamlessly interact with the physical world? That’s the magic of spatial computing, which blends the digital and physical environments to create immersive experiences. One key component of this technology is augmented reality, or AR. AR superimposes digital images, information, or objects onto your view of the real world through devices like smartphones, tablets, or smart glasses. Unlike virtual reality, which immerses you in a completely digital environment, AR enhances your current surroundings, making digital information feel like a natural part of your everyday life.
Augmented reality blends digital content with real-world environments for immersive, seamless experiences.
When you use AR, spatial orientation becomes essential. This is the system that helps digital objects understand where they are in your physical space and how they relate to your movements. With spatial orientation, digital content isn’t just overlaid randomly; it interacts intelligently with your environment. For example, when you point your phone at a piece of furniture, AR can display its dimensions, price, or reviews directly over the object. As you move around, the digital overlay adjusts in real time, maintaining proper alignment with the physical item. This seamless adaptation depends on sophisticated sensors and spatial mapping techniques that build a 3D model of your surroundings, allowing digital objects to stay anchored in specific locations.
Understanding how spatial orientation works is essential because it enables digital objects to behave as if they truly belong to the physical space. Imagine walking through a room where virtual furniture appears to be placed realistically on the floor or where digital characters move naturally as you approach them. This capability relies on spatial computing systems that track your position, orientation, and gestures, creating an intuitive interface that responds to your movements. By mastering spatial orientation, AR applications can deliver more immersive and accurate experiences, making digital content feel more tangible and integrated into your daily environment.
Additionally, advancements in sensor technology continue to enhance the precision and reliability of spatial orientation, broadening the range of applications for AR in everyday life. As you explore spatial computing, you’ll notice how augmented reality and spatial orientation work together to make digital interactions feel effortless. Whether you’re trying out new furniture before buying, navigating complex machinery with overlay instructions, or engaging with interactive educational content, these technologies work behind the scenes to connect your physical movements with digital responses. They bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds, making digital objects feel like they belong right where you are. With ongoing advancements, spatial orientation and AR are set to become even more precise, intuitive, and integrated, transforming how you interact with both digital content and the world around you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Secure Is My Data in Spatial Computing Environments?
Your data’s security in spatial computing environments depends on the platform’s measures. Usually, they use data encryption to protect your information during transmission and storage. User authentication adds an extra layer of security, ensuring only authorized individuals access your data. However, always stay cautious, keep software updated, and use strong, unique passwords to enhance safety, as no system is entirely foolproof.
Can Spatial Computing Be Used for Remote Collaboration?
Yes, spatial computing enables you to collaborate remotely in a virtual workspace, making real-time interaction seamless. You can share 3D models, visualize data, and communicate naturally as if you’re in the same room. This technology bridges distances, allowing you to work together efficiently, whether for design, training, or meetings. With spatial computing, remote collaboration becomes more immersive and productive, transforming how you connect with colleagues across the globe.
What Devices Are Required for Basic Spatial Computing?
You need to hit the ground running with a few key devices. AR glasses are essential, giving you a window into the digital world layered over your real environment. Motion controllers help you interact naturally and precisely within that space. Together, these tools make basic spatial computing accessible, turning your everyday surroundings into an interactive playground. With these devices, you’re all set to explore the exciting potential of spatial computing.
How Does Spatial Computing Impact Privacy Concerns?
Spatial computing raises privacy risks because devices collect and analyze your environment and activities. You might unknowingly share sensitive data, leading to potential misuse or breaches. To protect your privacy, guarantee data protection measures are in place, like encryption and secure storage. Stay informed about how your data is used, and consider adjusting device settings to limit data sharing, so you can enjoy spatial computing without compromising your privacy.
Is Spatial Computing Suitable for Children and Educational Purposes?
Spatial computing is suitable for children and educational purposes when you focus on child-friendly applications. You can integrate it effectively into educational settings, enhancing learning through interactive experiences. Just guarantee the content is age-appropriate and safe, and use platforms designed for young users. With proper supervision and suitable tools, spatial computing can boost engagement, creativity, and understanding, making learning more immersive and fun for children.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve got the basics of spatial computing, you’re ready to navigate this new digital frontier like a true explorer. Think of it as your personal holodeck, blending the virtual with reality, making everyday tasks more intuitive. As you experiment, remember that this technology is still evolving—kind of like a modern-day Gutenberg printing press. Embrace the journey, and soon you’ll be seamlessly blending worlds, one virtual step at a time.