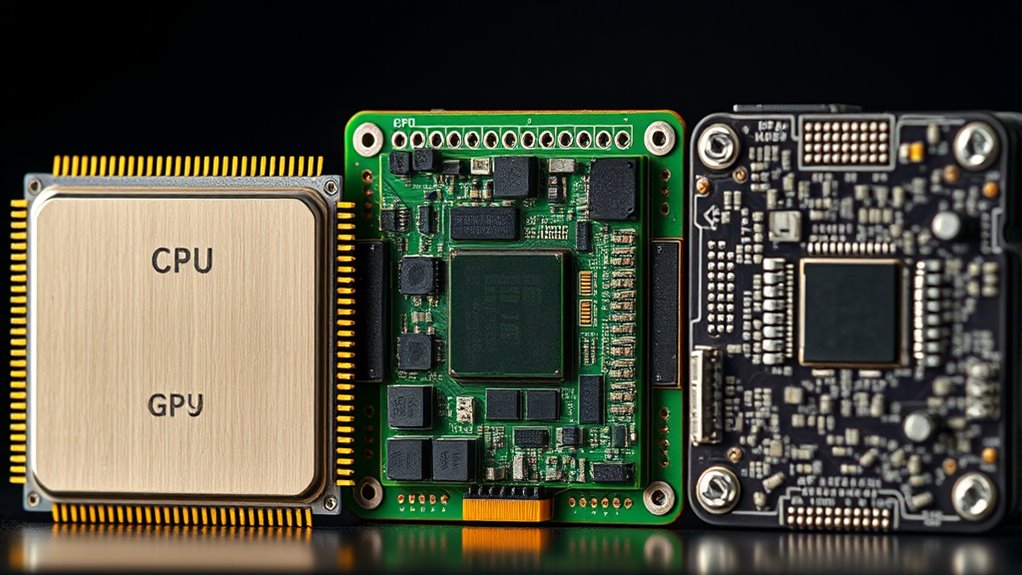
A CPU, GPU, and NPU are different types of processors that handle various tasks in your devices. The CPU, or central processing unit, manages general functions and multitasks like running your operating system. The GPU focuses on rendering images and videos, making graphics look smooth. The NPU is specialized for AI and machine learning, speeding up tasks like voice recognition or image analysis. If you’re curious about how these components work together, there’s more to explore ahead.
Key Takeaways
- CPU is the main processor managing general tasks and operating systems in a device.
- GPU specializes in rendering graphics, images, and videos through parallel processing.
- NPU is designed for AI and machine learning, accelerating neural network computations.
- Hardware integration ensures efficient communication among CPU, GPU, and NPU for optimal performance.
- Performance benchmarking evaluates each component’s speed, efficiency, and suitability for specific tasks.

Ever wondered what powers your devices and keeps everything running smoothly? It all comes down to the central components inside your computer or smartphone: the CPU, GPU, and NPU. These processors work together behind the scenes, each specialized for different tasks, guaranteeing your device performs efficiently. To truly understand how they contribute, it’s helpful to consider how hardware integration and performance benchmarking come into play. When manufacturers design these chips, they focus on seamless hardware integration, making sure each component communicates effectively. Performance benchmarking then measures how well these parts operate under various conditions, helping developers optimize their functions for speed, efficiency, and power consumption.
The CPU, or central processing unit, is often called the brain of your device. It handles most general tasks—running your operating system, managing files, and executing software instructions. Think of it as a versatile worker that can switch between different jobs quickly. Its architecture consists of multiple cores, which allow it to process several tasks simultaneously. When you open an app or browse the internet, the CPU’s performance benchmarking shows how fast it can process commands and handle multitasking. Proper hardware integration ensures that the CPU communicates effectively with other parts, such as memory and storage, to avoid bottlenecks. This harmony is essential for overall system responsiveness and stability. Developers often run performance benchmarks to compare different CPUs or to test new models, ensuring they meet desired standards before deployment. Additionally, optimizing hardware integration is crucial for enhancing overall device performance and user experience.
The CPU is the brain of your device, managing tasks and multitasking efficiently through advanced core architecture.
The GPU, or graphics processing unit, specializes in rendering images, videos, and 3D graphics. If you’re gaming, editing videos, or using applications that require intense visual processing, the GPU takes center stage. It’s designed to handle thousands of calculations simultaneously, making it ideal for parallel processing tasks. Performance benchmarking of GPUs focuses on frame rates, rendering quality, and their ability to handle complex visual effects smoothly. Hardware integration here means optimizing how the GPU works alongside the CPU and memory, reducing latency and increasing throughput. This tight coordination ensures that visual tasks are completed swiftly, providing a seamless experience whether you’re watching a movie or playing a high-end game.
In recent years, NPUs—or neural processing units—have emerged, tailored for AI and machine learning tasks. They accelerate neural network computations, making AI applications faster and more efficient. When integrating NPUs into devices, manufacturers prioritize hardware integration to guarantee they work harmoniously with CPUs and GPUs. Performance benchmarking for NPUs involves measuring how quickly they can process large datasets and run inference tasks, which is essential for applications like voice recognition, image analysis, and autonomous driving.

ARCTIC MX-4 (4 g) – Premium Performance Thermal Paste for All Processors (CPU, GPU – PC, PS4, Xbox), Very high Thermal Conductivity, Long Durability, Safe Application, Non-Conductive, Non-capacitive
CONSISTENT QUALITY: Our thermal paste packaging design has evolved over time, but the formula has remained the same,…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do CPUS, GPUS, and NPUS Work Together in Devices?
You see, CPUs handle general tasks, while GPUs excel at parallel processing for graphics and data-heavy work. NPUs specialize in AI tasks. They work together through hardware integration, sharing data efficiently to optimize performance. This collaboration guarantees your device runs smoothly, handling everything from gaming to AI applications seamlessly. By combining their strengths, these processors maximize speed and efficiency in modern devices, delivering a better user experience.
Which Chip Type Consumes the Most Power?
You might think GPUs consume the most power, but it’s actually NPUs that do. Their focus on AI tasks requires intensive power for deep learning workloads, leading to higher power consumption compared to CPUs and GPUs. When you compare efficiency, NPUs are less efficient per task but excel at specific AI functions. So, if power consumption is your concern, NPUs generally use more energy than CPUs or GPUs, especially during heavy AI processing.
Are NPUS Used in Everyday Consumer Electronics?
Yes, NPUs are used in everyday consumer electronics, especially in smartphones and wearable devices. You’ll find them integrated to boost AI performance, enabling features like voice recognition, image processing, and health monitoring. With smartphone integration, NPUs help speed up tasks without draining your battery, making your devices smarter and more responsive. Wearable device applications like fitness tracking and personal assistants also benefit from NPU technology for real-time, efficient AI processing.
Can a CPU Be Replaced by a GPU or NPU?
You can’t exactly replace your CPU with a GPU or NPU, but they work together like a team. The CPU vs GPU debate highlights how GPUs excel at parallel tasks, and NPUs shine in AI applications. While a GPU can handle some CPU tasks, it can’t fully replace the CPU’s versatile processing power. Similarly, NPUs are specialized for AI, complementing but not replacing the CPU in everyday tasks.
How Do I Choose the Right Processor for My Needs?
To choose the right processor, consider your performance needs—whether you prioritize gaming, video editing, or AI tasks—and opt for a CPU, GPU, or NPU accordingly. You should also evaluate compatibility considerations with your existing hardware and software. Balance your budget with the level of performance optimization required, ensuring the processor fits your system and future upgrades, so you get the best value and efficiency.

SAPLOS GT 730 4GB Graphics Card, Dual HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, DDR3 64-bit, Low Profile Video Card PC, DirectX 12, Computer GPU, Low Power, PCI Express x8
This 4gb graphics card powered by Kepler architecture, has 384 CUDA cores, get improved number of cores over…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
Now that you know what CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs are, imagine how these powerful processors might shape your future devices. As technology advances, the lines between them blur, revealing new possibilities you haven’t even dreamed of yet. Are you ready to see what’s next? Stay tuned—what comes next could change everything you thought you knew about computing. The future is closer than you think, and it’s more exciting than ever.

Toybrick TB-RK1808S0 AI Calculation Stick RK1808 NPU Processor for deep Learning Tools and a Separate Artificial Intelligence Accelerator
STRONG AIGORITHM PERFORMANCE : Built-in NPU power is up to 3.0 TOPs.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

MICRO CENTER CPU Motherbard Combo – core i5-14400 10cores Desktop Processor with Integrated UHD Graphics 730 and Gigabyte B760M DS3H AX DDR4 Motherboard
The Raptor Lake Refresh lineup offers 10 cores (6 P-cores + 4 E-cores) and 16 threads, well-suited for…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.